What the queue sharing group example for z/OS shows
This example shows the IBM MQ commands (MQSC) that we can use in IBM MQ for z/OS® for distributed queuing with queue sharing groups.
This example expands the payroll query scenario of the example in Message channel planning example for z/OS to show how to add higher availability of query processing by adding more serving applications to serve a shared queue.
The payroll query application is now connected to queue manager QM3 and puts a query to the remote queue 'PAYROLL QUERY' defined on QM3. This remote queue definition resolves to the shared queue 'PAYROLL' hosted by the queue managers in the queue sharing group QSG1. The payroll processing application now has two instances running, one connected to QM4 and one connected to QM5.
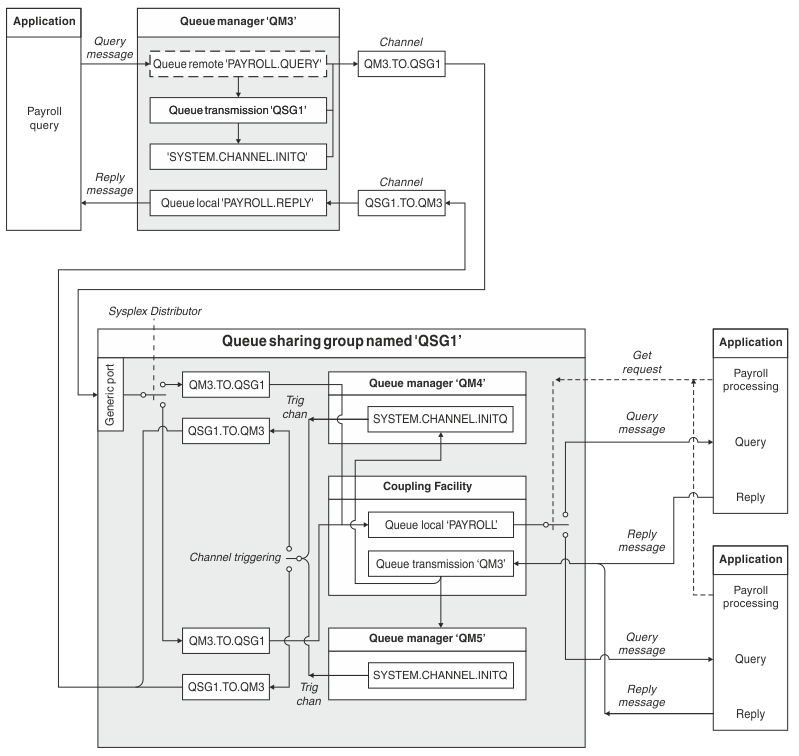
All three queue managers are assumed to be running on z/OS. In the example definitions for TCP/IP, QM4 has a VIPA address of MVSIP01 and QM5 has a VIPA address of MVSIP02. Both queue managers are listening on port 1414. The generic address that Sysplex Distributor provides for this group is QSG1.MVSIP. QM3 has a host address of 192.0.2.0 and is listening on port 1411.
In the example definitions for LU6.2, QM3 is listening on a symbolic luname called LUNAME1. The name of the generic resource defined for VTAM for the lunames listened on by QM4 and QM5 is LUQSG1. The example assumes that they are already defined on your z/OS system and are available for use. To define them see Defining yourself to the network using generic resources.
In this example QSG1 is the name of a queue sharing group, and queue managers QM4 and QM5 are the names of members of the group.