Configuration 2
Configuration 2 describes how queue sharing groups and intra-group queuing can be used, with no effect on the back-end payroll server application, to transfer messages between queue managers QMG1 and QMG3.
Configuration 2 shows a distributed queuing system that uses queue sharing groups and intra-group queuing to transfer messages from the payroll request application to the payroll server. This configuration removes the need for channel definitions between queue managers QMG2 and QMG3 because intra-group queuing is used to transfer messages between these two queue managers.
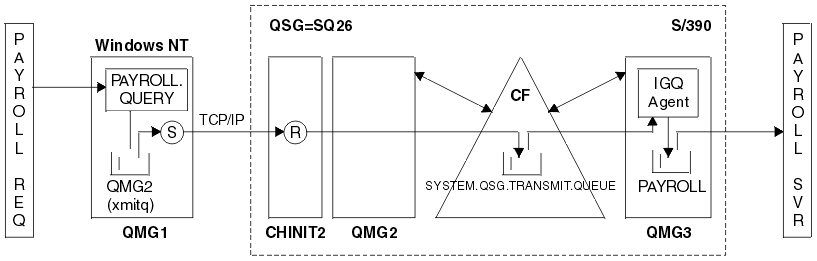
The flow of operations is as follows:
- A query is entered using the payroll request application connected to queue manager QMG1.
- The payroll request application puts the query on to remote queue PAYROLL.QUERY. As queue PAYROLL.QUERY resolves to transmission queue QMG2, the query is put on to transmission queue QMG2.
- Sender channel (S) on queue manager QMG1 delivers the query to the partner receiver channel (R) on queue manager QMG2.
- Receiver channel (R) on queue manager QMG2 puts the query on to queue PAYROLL on queue manager QMG3. As queue PAYROLL on QMG3 resolves to shared transmission queue SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE, the query is put on to shared transmission queue SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE.
- IGQ agent on queue manager QMG3 retrieves the query from shared transmission queue SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE, and puts it on to local queue PAYROLL on queue manager QMG3.
- The payroll server application connected to queue manager QMG3 retrieves the query from local queue PAYROLL, processes it, and generates a suitable reply.