Intra-group queuing concepts
Intra-group queuing can be used to deliver, more efficiently, small messages to queues residing on remote queue managers within a queue sharing group.
Intra-group queuing (IGQ) can effect potentially fast and less-expensive small message transfer between queue managers within a queue sharing group (QSG), without the need to define channels between the queue managers.
The following diagram shows a typical example of intra-group queuing.
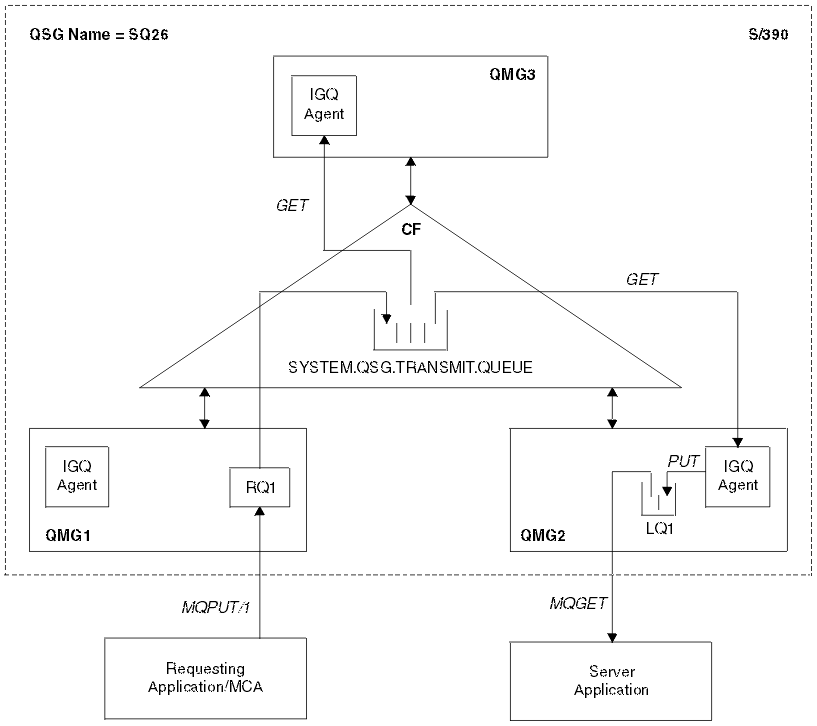
The diagram shows:
- IGQ agents running on three queue managers (QMG1, QMG2, and QMG3) that are defined to a queue sharing group called SQ26.
- Shared transmission queue SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE that is defined in the coupling facility (CF).
- A remote queue definition that is defined in queue manager QMG1.
- A local queue that is defined in queue manager QMG2.
- A requesting application (this application could be a Message Channel Agent (MCA)) that is connected to queue manager QMG1.
- A server application that is connected to queue manager QMG2.
- A request message being placed on to the SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE.
Intra-group queuing and the intra-group queuing agent
An IGQ agent is started during queue manager initialization. When applications open and put messages to remote queues, the local queue manager determines whether intra-group queuing is used for message transfer. If intra-group queuing is to be used, the local queue manager places the message on to the SYSTEM.QSG.TRANSMIT.QUEUE. The IGQ agent on the target remote queue manager retrieves the message and places it on to the destination queue.